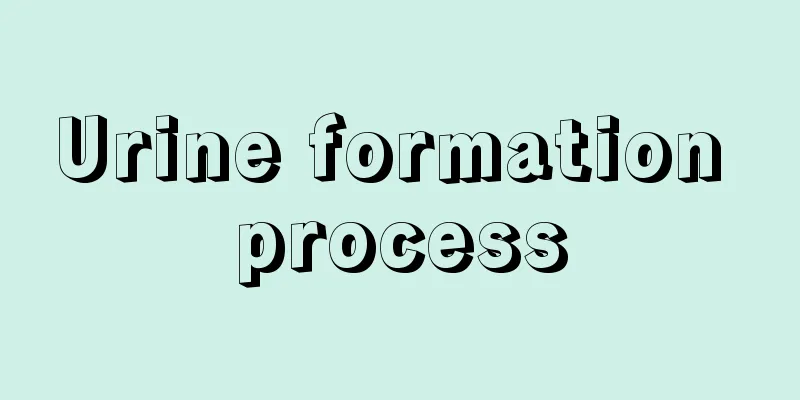
Urine formation process
|
The most obvious activity of metabolism is excretion. Excretion has a lot to do with our physical condition. If we are constipated, our stomach will feel bloated all day long, and even our face will appear oily and have acne. One of the excretions is urination. Drinking water will produce a feeling of urination, and urination is beneficial to the smooth functioning of our body functions. So, how is urine formed after drinking water? Urine production refers to the filtration of plasma components within the glomerular capillary network into the renal capsule cavity. The driving force of filtration is the effective filtration pressure of the glomerulus. The structural basis of filtration is the filtration membrane, which is composed of the endothelial cells of the glomerular capillaries, the basement membrane and the visceral epithelial cells of the renal capsule (also known as podocytes). The human filtration membrane is approximately 325 nanometers (nm) thick, with the endothelial cell and podocyte layers each approximately 40 nm thick. There are regularly distributed pores on the endothelial cells with a pore diameter of 50 to 100 nanometers. The total area of the pores accounts for 5 to 10% of the total area of the capillaries, while the total area of the pores of the muscle capillaries accounts for 0.2% of the total area of the capillaries. Therefore, the permeability of the former is 100 times or more greater than that of the latter. The basement membrane is a microfiber network composed of hydrated gel with a pore size of 4 to 8 nanometers and great stretchability. Podocytes are cells with protrusions. Primary protrusions extend from the cell body, and the latter extend secondary protrusions, forming a finger-like cross with the protrusions of adjacent podocytes. The gap between the protrusions is called the slit, with a pore diameter of 25 nanometers. It is covered with a thin film called the slit membrane, which is the last barrier for material filtration. The structure of the filter membrane is like a multi-layer sieve. It has a certain permeability and constitutes a mechanical barrier of the filter membrane, limiting the passage of large molecules. The process is as follows: 1. Glomerular filtration It refers to the process in which water, inorganic ions and small molecular solutes in plasma are filtered into the renal capsule through the filtration membrane to form glomerular filtrate (primary urine) when blood flows through the glomerular capillaries. Except for a very small amount of protein, the concentration, osmotic pressure and pH of the other components in the filtrate are close to those of plasma. However, blood cells and large molecular plasma proteins cannot be filtered into the renal capsule cavity and remain in the blood. 2. Reabsorption in the renal tubules and collecting ducts When the primary urine flows through the renal tubules and collecting ducts, the water and various solutes in it completely or partially pass through the tubular epithelial cells and re-enter the surrounding capillary blood. Because the structures of each segment of the renal tubule and the collecting duct are unique, the reabsorption capacity varies greatly. The proximal tubule has the strongest reabsorption capacity, and almost all nutrients in the primary urine are absorbed in the proximal tubule. In addition, most of the water and electrolytes in the primary urine and some urea, uric acid, etc. are also reabsorbed in this section. 3. Secretion and excretion of renal tubules and collecting ducts The process by which the renal tubular and collecting duct epithelial cells excrete metabolic products or certain substances in the blood into the tubular fluid is called secretion and excretion. It mainly includes secretion of H+, secretion of K+, and secretion of NH3. Other substances in plasma such as creatinine and para-aminohippuric acid can also be discharged into the lumen. In addition, certain substances that enter the body, such as penicillin, phenol red, etc., are also mainly excreted through the renal tubules. The excretion of the above substances mostly takes place in the proximal tubule. |
>>: What to do if the humidity at home is too high
Recommend
Is there any harm to pregnant women after rectal cancer radiation?
The embryo is most sensitive to radiation within ...
Four types of parasols do not protect against the sun
Although the early autumn sunshine is less sharp ...
Does short hair make your face look bigger?
When it comes to short hair, everyone must think ...
Symptoms of cervical lymphadenoma
Lymph is one of the most common lymph nodes in th...
How to relieve shoulder nerve pain?
Many friends who overwork are prone to shoulder n...
What should I do if my porcelain teeth ache?
From a clinical perspective, if a porcelain tooth...
A 45-year-old man died of liver cancer. He didn’t smoke or drink and had a light diet. The doctor sighed: This is too harmful to the liver
In my career, every patient's death is a heav...
Women should pay attention to the causes of ovarian cancer
In recent years, the incidence of ovarian cancer ...
What to do if the apex of the lung becomes inflamed
The lungs are very important to people's bodi...
What are the dangers of artificial hair transplantation?
Artificial hair transplantation is a relatively c...
Treatment of acute urethritis
There are many methods for the treatment of acute...
Can childhood skin cancer be cured?
Can skin cancer in children be cured? To know the...
Pancreatic cancer patients have flushing on their faces
If pancreatic cancer patients experience facial f...
What is fundus erythematosus? How to prevent
Fundus erythema is an eye disease that is more co...
How to get rid of hair without it growing back
The surface of the human body is not smooth, but ...