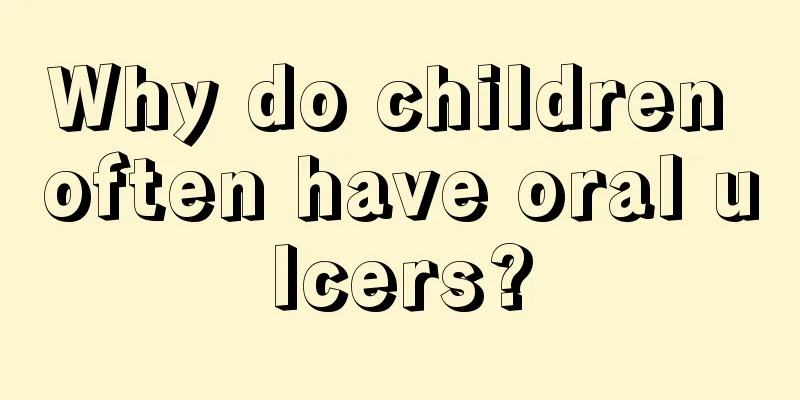Human kidney structure

|
For some people who study medicine and biology, they may have a more comprehensive understanding of the structure of the human body, but for some people who study Chinese, they know nothing about the structure of the human body and have only been exposed to some biological knowledge in junior high school and high school. The kidney is a very important organ for us. Everyone has two kidneys, on both sides of our waist. So what is the structure of the human body? 1. Kidneys One of the five internal organs, it is located behind the waist, on both sides of the spine, one on each side. It is a dark red solid organ, shaped like a broad bean. The surface of the kidney is smooth and can be divided into upper and lower ends, front and back surfaces, and inner and outer edges. In the human body, normal adults have two kidneys. The main physiological functions are to store essence, control growth and development and reproduction, control water and absorb air, and it is closely related to bones, marrow and ears. The kidneys are part of the urinary system and are responsible for filtering impurities from the blood, maintaining the balance of body fluids and electrolytes, and finally producing urine which is excreted from the body through subsequent pipes. They also have endocrine functions to regulate blood pressure. It is said in Suwen: "The waist is the home of the kidneys." Because the kidneys store the "innate essence", are the basis of the yin and yang of the internal organs and the source of life, they are called the "innate basis". Kidneys are also commonly known as kidneys. 2. The specific shape of the kidney The kidneys are paired, lenticular organs located in shallow recesses on either side of the spine behind the peritoneum. It is about 10-12 cm long, 5-6 cm wide, 3-4 cm thick, and weighs 120-150 grams. The left kidney is slightly larger than the right kidney. The upper end of the kidney's longitudinal axis is inward and the lower end is outward. Therefore, the upper poles of the two kidneys are closer and the lower poles are farther apart. The angle between the kidney's longitudinal axis and the spine is about 30 degrees. Renal hilum, renal pedicle, and renal sinus: The outer edge of the kidney is convex, and the middle part of the inner edge is concave, called the renal hilum. It is mostly quadrilateral, and its edge is called the renal lip. The front lip and the back lip have a certain degree of elasticity. It is the gateway for the renal pelvis, blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels to enter and exit. All blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels enter the kidney through here, and the renal pelvis exits the kidney through here. These structures entering and exiting the renal hilum are wrapped by connective tissue, and this part of the structure is collectively called the renal pedicle. There is a larger cavity inside the kidney from the renal hilum, called the renal sinus. The renal sinus is surrounded by renal parenchyma and contains the renal artery, renal vein, lymphatic vessels, renal calyces, renal calyces, renal pelvis and adipose tissue. 3. Specific location of kidneys The kidneys are located on both sides of the spine, close to the posterior abdominal wall, and behind the peritoneum. The right renal hilum is aligned with the transverse process of the second lumbar vertebra, and the left one is aligned with the transverse process of the first lumbar vertebra. The right kidney is slightly lower than the left kidney by 1-2 cm due to the relationship with the liver. The normal up and down movement of the kidney is within the range of 1-2 cm. The kidneys are below the diaphragm. During physical examination, except for the lower pole of the right kidney which can be palpated at the lower edge of the ribs, the left kidney is difficult to palpate. 4. The internal structure of the kidney It is divided into two parts: renal parenchyma and renal pelvis. In the longitudinal section of the kidney, we can see that the renal parenchyma is divided into two layers: the outer layer is the cortex and the inner layer is the medulla. (1) Renal cortex: It is reddish brown when fresh and is composed of glomeruli and convoluted tubules. Part of the cortex extends into the inter-pyramidal space of the medulla to become renal columns. (2) Renal medulla: It is light red in color when fresh and is composed of 10-20 cones. The renal pyramid is triangular in cross section. The base of the cone faces the convex surface of the kidney, and the tip faces the renal hilum. The main tissue of the cone is the collecting duct. The tip of the cone is called the renal papilla. Each papilla has 10-20 papillary ducts that open into the infundibulum of the renal calyx. In the renal sinus are the calyces, which are funnel-shaped membranous tubules surrounding the renal papillae. The renal pyramids are connected to the renal calyces. Each kidney has 7 to 8 calyces, and 2 to 3 adjacent calyces combine to form a major calyx. Each kidney has 2 to 3 calyces, which merge into a flat funnel-shaped renal pelvis. After the renal pelvis exits the renal hilum, it gradually narrows and becomes thinner and transforms into the ureter. |
<<: How to grow nose hair when you have less nose hair
>>: How big is the risk of rhinoplasty
Recommend
What to do if your hands get spicy after washing chili peppers
Cooking is a very tedious process, but you can al...
What to do before going to bed to help you sleep
Many people always find themselves unable to slee...
How long can clams be kept in the refrigerator
Clams are an increasingly popular seafood food an...
What should I do if I get red spots on my face due to allergies
Many people are prone to red spots on the face du...
Advantages and disadvantages of essential oils for weight loss
In life, many people go to beauty salons to lose ...
Can people with gallstones eat bayberry
Most young people nowadays like to stay up late. ...
What is the reason for stomach pain and swelling
There are many reasons in life that may cause a p...
What to do if blisters appear after being bitten by fleas
Nowadays, with the improvement of people's li...
5 typical symptoms of ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer refers to a malignant tumor that o...
What are the benefits of drinking more water
In life, everyone knows that water is the source ...
What cuisine does Zhejiang cuisine belong to
In Chinese culture, different places have differe...
Why does the duck egg white turn green?
When eating duck eggs, especially salted duck egg...
What to do about hair loss? Eat more of these 6 foods to prevent hair loss
In addition to affecting a person's appearanc...
What are the early symptoms of tongue cancer? If you experience these 5 symptoms, you should seek medical attention immediately
The most easily discovered symptom of early tongu...
How do you get prostate cancer
How is prostate cancer caused? Generally speaking...