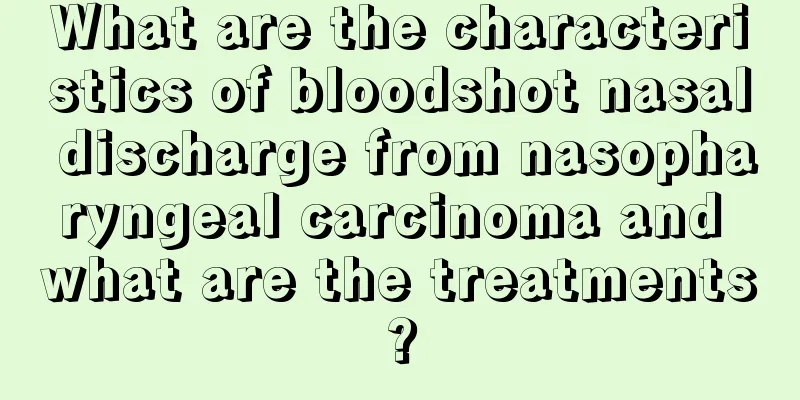Meniscus white area

|
As the name suggests, the meniscus is shaped like a half moon. The meniscus is located above our tibial joint. The meniscus is a kind of cartilage tissue. There are so-called red and white areas on the meniscus. In fact, the red area is the area with blood supply, while the white area has no blood supply. Therefore, when the white area of the meniscus is injured, it has no ability to recover on its own. Where is the white area of the meniscus In the cross section of the meniscus, the 1/3 close to the joint capsule is the red area, which means it has blood supply, the middle 1/3 has no red or white area, which means it has partial blood supply, and the inner 1/3 is the white area, which has no blood supply. Symptoms of meniscus injury 1. Tenderness The location of tenderness is generally the location of the lesion, which is important for the diagnosis of meniscus injury and the determination of its injury site. During the examination, place the knee in a semi-flexed position, and press point by point from front to back with the thumb along the upper edge of the tibial condyle, i.e. the edge of the meniscus, in the medial and lateral gaps of the knee joint. There will be fixed tenderness at the site of meniscus injury. At the same time, when the knee is passively flexed or extended or the leg is internally or externally rotated, the pain is more obvious, and sometimes abnormal movement of the meniscus can also be felt. 2. McFarland test The patient lies on his back, and the examiner holds the calf ankle with one hand and the knee with the other hand to flex the hip and knee as much as possible, and then abducts, externally rotates and abducts, internally rotates, or adducts, internally rotates, or adducts and externally rotates the calf, and gradually straightens it. The test is positive if pain or sound occurs, and the location of the injury is determined based on the location of the pain and sound. 3. Strong hyperextension or hyperflexion test If the knee joint is passively hyperextended or hyperflexed, such as if the anterior meniscus is injured, hyperextension may cause pain; such as if the posterior meniscus is injured, hyperflexion may cause pain. 4. Lateral pressure test With the knee in extended position, forcefully passively adduct or abduct the knee. If there is a meniscus injury, pain will be caused by compression in the joint space on the affected side. 5. Single-leg squat test Use one leg to gradually and cautiously squat down from a standing position, and then stand up from a squatting position. The opposite side is normal, and the affected side squats or stands in a certain posture. Due to meniscus injury caused by compression, joint pain may cause you to be unable to squat or stand up. 6. Gravity test The patient takes a side-lying position and lifts his lower limbs to perform active flexion and extension of the knee joint. When the joint space on the affected side is downward, pain will be caused by compression of the damaged meniscus; conversely, when the joint space on the affected side is upward, there will be no pain. |
<<: Precautions for holding urine during test tube transplantation
>>: Degeneration of the posterior horn of meniscus
Recommend
What are the hazards of osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma is familiar to everyone. It is a com...
Are there any dangers of using a yoga neti pot?
Yoga is a very commonly used exercise technique i...
Can the saliva of kidney cancer patients be contagious?
Is the saliva of kidney cancer patients contagiou...
Is frequent constipation a symptom of colon cancer? The difference between common constipation and colon cancer constipation
Is frequent constipation a symptom of colorectal ...
How harmful is hair transplant?
Nowadays, more and more people are suffering from...
Is axillary lymph node dissection necessary for breast cancer?
Radiotherapy is needed after surgery to prevent c...
What are the symptoms of low thyroid hormone?
Thyroid disease is directly related to the health...
Tips for meeting your mother-in-law for the first time
If your relationship develops to the point where ...
What are the symptoms of pancreatic discomfort
The pancreas is an inconspicuous organ in our bod...
Early symptoms of nasopharyngeal cancer
Throat cancer is a common disease in life, but mo...
Can bitter melon and onion be eaten together
Bitter melon is a very nutritious vegetable. The ...
What should I do if my total cholesterol is high
There are many types of cholesterol, which is a t...
What should I do if white clothes turn yellow?
Everyone likes to wear white clothes in the summe...
What is the reason for calf soreness
After regular running exercises, the calves are p...
What to do if my waist hurts from holding a baby
Since babies do not have normal mobility after bi...