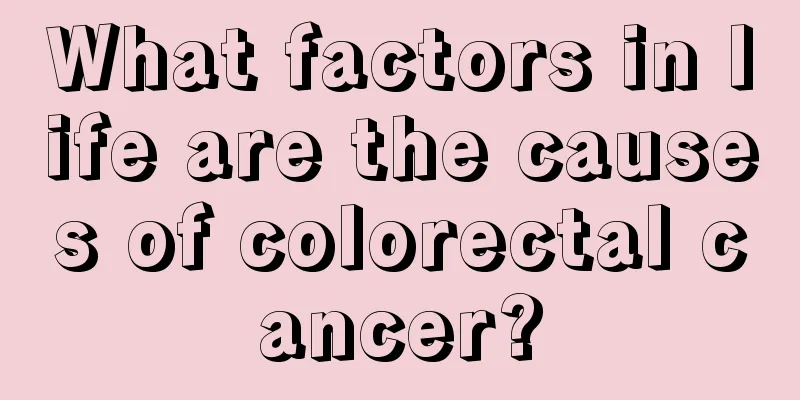Histopathological grading of breast cancer

|
Breast cancer is a highly heterogeneous disease. Clinical and pathological classifications have long been used to guide patient treatment. Although classic histopathological classification remains important, molecular characterization of breast cancer has rapidly become an important tool for understanding clinical prognosis and predicting chemotherapy efficacy. Classical histopathological grading Based on cell morphology, breast cancer is usually divided into tumors that originate from ductal cells (ductal adenocarcinoma) or lobules (lobular carcinoma). Breast malignancies are further divided into invasive cancers that can metastasize (invasive carcinoma) and non-invasive cancers confined to the basement membrane (ductal carcinoma in situ, i.e. intraductal carcinoma). 1. Ductal adenocarcinoma is the most common tissue type. The clinical prognosis varies widely, from indolent to rapidly progressive. The prognosis can be assessed by cell morphological characteristics and the expression of molecular markers such as ER, HER2, Ki67 and HER2. 2. Lobular carcinoma Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) can increase the risk of developing invasive cancer (ductal carcinoma or lobular carcinoma) in the future. However, LCIS itself has no clinical consequences. Similar to invasive ductal carcinoma, invasive lobular carcinoma can metastasize, and its stage is related to prognosis. The diagnosis of invasive lobular carcinoma is particularly difficult due to the unique single-cell radial invasion pattern, which often results in negative findings on palpation or breast imaging. Compared with invasive ductal carcinoma, invasive lobular carcinoma tends to occur bilaterally and is prone to metastasize to the pleuropericardial surface. 3. Special subtypes with better prognosis include papillary, tubular, mucinous and medullary carcinomas. 4. Inflammatory breast cancer is a highly invasive subtype. Invasion of the skin lymphatic vessels can be observed under a microscope, which confirms the diagnosis. Clinically, it is often accompanied by breast skin erythema (similar to mastitis) and skin edema, also known as "orange peel-like lesions." 5. Paget's disease of the breast is characterized by unilateral nipple eczematous changes, often accompanied by ductal carcinoma in situ. 6. Cystosarcoma phyllodes is very rare and mostly benign, accounting for less than 1% of all breast tumors. About 90% of phyllodes tumors are benign, and about 10% are malignant. Metastasis of this type of tumor is rare, but it can recur locally and requires surgical resection with wide margins to effectively control local recurrence. 7. Rare tumors include squamous cell carcinoma, lymphoma and sarcoma. |
<<: What are the ways to check for breast cancer
>>: How to detect breast cancer
Recommend
What are the dangers of general anesthesia for surgery
It is necessary to give anesthesia before surgery...
There are several simple and effective ways to treat bad breath
Bad breath is familiar to many people in life, an...
How long can pork be refrigerated?
Pork is a type of meat that we often eat nowadays...
Bananas cause coldness and poor spleen and stomach, so eat less
Banana is a very common fruit in our daily life a...
How to diagnose pancreatic cancer
The diagnosis of pancreatic cancer requires very ...
Is pasta easy to digest?
Pasta should be easily digestible and acceptable ...
Will washing your face with fluoride-containing water cause acne?
The most annoying thing for everyone is acne on t...
Can I take a shower if I'm sweaty?
In the summer, many people like to take a cold sh...
What are the causative factors of secondary liver cancer
Usually, secondary liver cancer is not caused by ...
How many months should the pentavalent vaccine be started?
Vaccine is a great invention in modern life. This...
Is nail disease onychomycosis? What are the symptoms
Generally, human nails will not get sick because ...
Seasonal rhinitis
Everyone should know about rhinitis. Many people ...
What medicine is good for social phobia
It is a neurological disorder that makes it diffi...
What can I eat to boost my immunity?
Everyone should pay attention to physical immunit...
The latest progress in cellular immunotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Recent progress in cellular immunotherapy for nas...