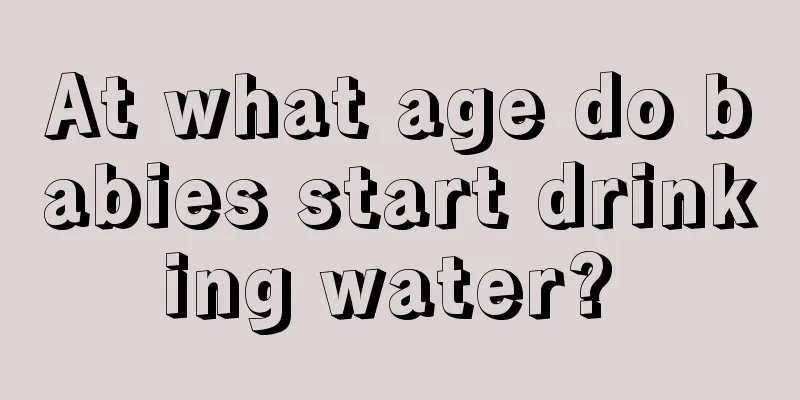Three histological types of astrocytoma

|
Astrocytomas are tumors composed of astrocytes. They are relatively common central brain tumors that can grow anywhere in the brain or spinal cord. Most adult astrocytomas grow in the cerebrum, while pediatric astrocytomas often grow in the cerebellum and brainstem. Astrocytomas can be divided into three subtypes histologically. 1. Fibrous type: This is the most common type and can be found in almost any part of the central nervous system, but it is mostly concentrated in the cerebral hemispheres in adults and more common in the cerebellum, brainstem and thalamus in children and adolescents. This type of fibrous brain tumor is very hard, sometimes a little elastic like rubber, with abundant blood vessels in the tumor tissue, and no proliferation of vascular endothelial cells. The interstitium may be calcified, and the adjacent cerebral cortex may be infiltrated by the tumor and become dark gray. Cysts of different sizes and shapes may form in the center of the tumor. 2. Obese cell type: This type is relatively rare, accounting for about 25% of astrocytomas. It is usually found in the cerebral hemispheres and also in the septum pellucida. The tumor grows in an infiltrative manner and grows rapidly. Small cysts may form on the surface of the tumor and the texture is soft. Obese cells observed under a microscope are enlarged, spherical or polygonal, with uniform and transparent cytoplasm and short and thick protrusions. The nucleus of the tumor is very small, the nucleolus is not obvious, the nuclear division is rare, and the cytoplasm is foamy and abundant. 3. Protoplasmic type: This is the rarest type, usually located in the temporal lobe of the brain. The invasion site of protoplasmic cancer is relatively superficial, mainly in the cerebral cortex, and the distance between the affected gyri widens and becomes flat. When it is a little more serious, the cancer can invade the white matter and develop deeply in an infiltrative manner, forming cystic tissues of varying sizes, numbers and shapes. The hemisection of the tumor is generally translucent and uniformly jelly-like. |
<<: TCM Syndrome Differentiation and Treatment of Gallbladder Cancer
>>: Patients with ovarian cancer and diabetes should control blood sugar before surgery
Recommend
Postoperative care issues for breast cancer
Surgical resection is one of the key measures for...
How to remove static electricity from cars in winter
Static electricity is mostly generated when the w...
What medicine to take for genital folliculitis
Hair follicles are very important things in the b...
The efficacy and function of wenwan walnuts
Walnut is a kind of dried fruit that we often eat...
Viral fever
Fever is a very common phenomenon. In daily life,...
What is tenosynovitis? It actually has these symptoms
Tenosynovitis can be caused by injury, overuse (e...
What are the dangers of nasal vestibule cyst?
Vestibular cyst is a common nasal disease. The in...
What are the famous snacks in the country
Food is the most important thing for people. Peop...
What to eat during bone cancer chemotherapy? Three types of food are essential
As we all know, bone cancer is a very terrible di...
What is the current situation of small cell lung cancer
Small cell lung cancer is a type of bronchial lun...
Is upper gastrointestinal tract radiography painful?
Upper gastrointestinal tract radiography is one o...
What imported medicine is good for nasopharyngeal carcinoma
What imported medicine is good for nasopharyngeal...
Scalp injections for hair loss treatment
In order to quickly cure the annoying hair loss, ...
There are a lot of red bloodshot on the thighs
Some people find that there are some red blood st...
What are the hazards of fluorescent agents
What are the hazards of fluorescent agents? In fa...