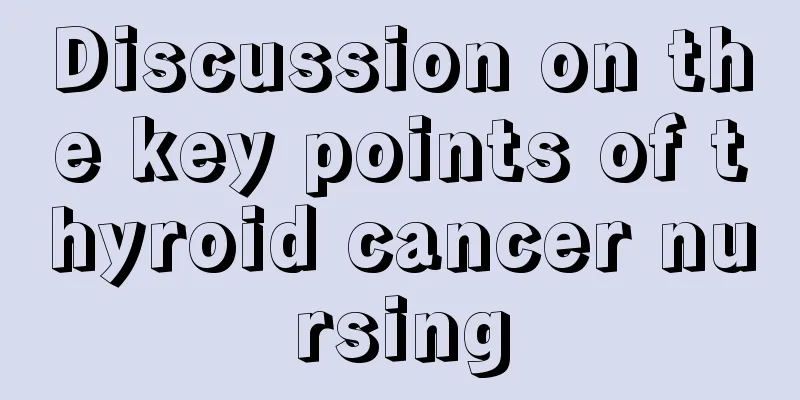Gallbladder cancer metastasis pathway

|
Gallbladder cancer can spread in many ways, including direct invasion, lymphatic, hematogenous, along the neurovascular plexus, intraperitoneal implantation, and intrabiliary dissemination. Direct invasion (liver and surrounding organs) and lymphatic metastasis are the main ways of metastasis of gallbladder cancer. Among confirmed cases of gallbladder cancer, only about 25% of the tumors are confined to the gallbladder wall. 35% have local lymph node metastasis or invade adjacent organs such as the liver, and 40% have distant lymph node or organ metastasis. 1. Direct invasion accounts for 65%-90%. Because the gallbladder wall on one side of the gallbladder bed has no serosal layer, it is common for gallbladder cancer to directly invade the liver (segments IV and V) through the gallbladder bed. At the same time, because the gallbladder venous plexus directly flows back into the nearby liver, the tumor can directly invade the liver parenchyma along the vascular nerve plexus, and in the late stage, it can also cause distant metastasis in the liver or distant organ metastasis through the bloodstream. The tumor can directly invade the adjacent organs around the gallbladder (common bile duct, gastric antrum, duodenum, pancreas and transverse colon, etc.), or spread up and down along the hepatoduodenal ligament through the vascular nerve plexus, directly invade the extrahepatic bile duct or metastasis to the lymph nodes around the liver portal to compress the common bile duct and cause obstructive jaundice. 2. Lymph node metastasis accounts for 40%-85%. When the gallbladder muscle layer is affected, lymph node metastasis may occur. The pattern and range of lymph node metastasis of gallbladder cancer are consistent with the lymphatic drainage pathway of the gallbladder. The vast majority of lymph node metastasis first occurs in the bile duct lymph nodes, followed by the common bile duct lymph nodes and the liver portal lymph nodes, and finally metastasizes to other regional lymph nodes: peripancreatic, periduodenal, periportal vein, celiac trunk, and lymph nodes around the superior mesenteric artery. A few can retrogradely metastasize upward to the liver portal. 3. Hematogenous metastasis accounts for 20%-25%, returning to the quadratic lobe of the liver through the deep vein of the gallbladder, manifesting as a local mass in the liver near the primary lesion, with or without satellite nodules; lung metastasis is less common. 4. Spread along nerves accounts for 10%-15%. It can spread along the nerve plexus in the gallbladder wall or the hepatoduodenal ligament. 5. Spread into the bile duct is rare. The tumor descends along the gallbladder neck to the common bile duct and implants in the neck and the inner wall of the common bile duct. Cancerous tissue may also fall off and enter the common bile duct, causing obstructive jaundice. 6. Abdominal implantation is rare, but rupture or perforation of gallbladder cancer can lead to extensive abdominal implantation. |
<<: Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment for Laryngeal Cancer
>>: Clinical symptoms of pancreatic cancer
Recommend
Red bags under the eyes
When people lack sleep, or smoke or drink, it is ...
How many days does it usually take for bruised eyes to recover?
Because of the trauma, subcutaneous bleeding will...
What is the reason for white millet grains coming out of the face
Nowadays, many female friends are particularly fo...
Why do pimples appear more the more you squeeze them
Many people know that pimples will get bigger the...
Indications for potassium chloride solution
Potassium chloride solution is often used to trea...
Is it good to wash your face with homemade soap?
Soap and perfumed soap are often used in our live...
Will lymphadenitis turn into lymphoma?
Can lymphadenitis turn into lymphoma? 1. Lymphade...
A few years of chemotherapy for prostate cancer 10 courses of treatment
How many years does it take to complete 10 course...
What foods are better for preventing liver cancer? 9 kinds of foods to eat more to prevent liver cancer
Everyone knows that the incidence of liver cancer...
What is the reason for acne on the back
Nowadays, many people pay attention to the acne o...
What to do if you have a sore throat due to inflammation
Getting a sore throat due to heat is a very commo...
Can early cervical cancer be detected through gynecological examination?
Early cervical cancer can be detected through gyn...
Can Panax notoginseng powder beautify and remove freckles?
Panax notoginseng is a very common medicine in li...
How to remove oil stains from clothes
Everyone can have a clean and tidy image, which w...
Environmental factors are one of the main causes of colorectal cancer
The cause of colorectal cancer has always been so...